Urine analysis
A guide explaining the results of urine tests.
The blood in the human body is filtered through the kidneys about 2x an hour, producing about 150 liters of first urine per day. 99% of the first urine is absorbed back into the blood, leaving 1.5 liters of urine per day.
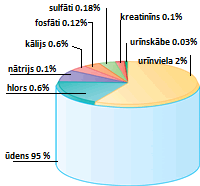
Urine composition.
Urine analysis is used as a monitoring and / or diagnostic method for several diseases, eg:
- urinary tract infections;
- kidney stones;
- various kidney diseases;
- diabetes and high blood pressure (hypertension, etc.)
Urine tests are prescribed to a wide range of patients in order to detect changes in the state of health in a timely manner, e.g. Elevated levels of protein and sugar (glucose) are found in the urine before a person feels unwell.
The results of the tests, in the case of diseases, do not indicate the exact cause of the disease, nor do they determine whether the disease is acute or chronic. They complement blood tests and help to more accurately determine or confirm the patient's diagnosis.
As a number of diseases do not show changes in the urine at an early stage, results with 'no abnormalities' do not mean that the patient is healthy.
The doctor's task is to understand the correlation between the patient's symptoms, blood biochemical analysis, complete blood count and urine test results.
There are 3 steps to completing a urine test:
1) physical parameters (color, clarity, specific gravity, pH);
2) chemical parameters (form elements, nitrite test, proteins, glucose, ketones, urobilinogen, bilirubin, Hb);
Microscopy (leukocytes, erythrocytes, epithelium, cylinders, mucus, salts, bacteria, etc.)
Physical characteristics
Color
Normal: light yellow to dark yellow
Deviation:
|
without color |
this may be due to long-term kidney disease or uncontrolled diabetes |
|
dark yellow |
the cause may be dehydration |
|
reddish |
the cause may be blood in the urine |
Color is affected by food, medication, disease. A light or dark hue indicates the amount of water in the urine - the darker the less water. Vitamin B, as a dietary supplement, stains the urine bright yellow. Some medications, beets, rhubarb or blood color the urine reddish brown.
Clarity
Normal: clear
Deviation:
|
smoky, cloudy |
this can be caused by bacterial, blood, semen, yeast, crystals, mucus or parasitic infections (eg trichomonas) |
Specific weight
Norma: 1.005–1.030
Deviation:
|
very high |
concentrated urine and shows: (a) too little water has been used; b) too much water has been lost (through vomiting, sweating, diarrhea); (c) the urine contains sugar or protein. |
|
very low |
diluted urine, which may occur: (a) drinking too much fluid; (b) certain kidney diseases; (c) the use of diuretics; (d) may be due to uncontrolled diabetes or fasting. |
The specific gravity shows whether the kidneys balance the amount of water in the urine well, i.e. the test determines how much substance is in the urine in addition to the water. The higher the value, the more concentrated the urine test material. If you drink a lot of water, the kidneys replenish the urine with water, reducing the specific weight of the urine. When water is drunk a little, the kidneys produce urine with a small amount of water, which has a high specific gravity.
pH
|
Norma: |
4.8–7.4 |
Deviation:
|
High |
may be diagnosed with vomiting, kidney disease, urinary tract infections and asthma; |
|
low |
in lung disease, uncontrolled diabetes, aspirin overdose, diarrhea, dehydration, fasting, alcohol overdose with ethylene glycol (antifreeze). |
pH indicates how acidic or alkaline urine is. Urine pH 4 is strongly acidic, pH 7 is neutral, pH 9 is very alkaline.
Urine pH is affected by medicines and food - especially citrus fruits and dairy products (eg to avoid the formation of certain kidney stones
Smell
in examinations is not singled out as a separate parameter.
Urine does not smell strong, but some diseases, foods, vitamins and antibiotics can affect its smell.
Deviation for some diseases:
|
unpleasant |
may be caused by E.coli bacteria and urinary tract infections |
|
sweet, fruity |
the cause may be uncontrolled diabetes or fasting |
|
syrup |
indicate that the body does not break down certain amino acids |
Chemical parameters
Form elements
Norma: <25 / μL
Deviation:
|
above 25/μL |
inflammation of the urinary tract or kidneys. |
Nitrite test
Norm: negative
Deviation:
|
positive |
urinary tract infection (a bacterium that causes inflammation forms an enzyme that converts urinary nitrates into nitrites). In addition, urine inoculation should be performed to determine AB sensitivity (i.e., which group of antibiotics may be used to treat the infection). |
Protein
Normal: not found or <0.25 g / L
Deviation:
|
above 0,25 g/L |
renal impairment; |
|
found |
may mean: kidney damage, infection, cancer, high blood pressure, diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, nephromerulonephritis (inflammation of the lumps of the kidneys); may indicate: heart failure, leukemia, mercury poisoning or mercury; |
|
Found for prengant |
may indicate: heart failure, preeclampsia, eclampsia. |
Protein is not usually found in the urine, but fever, high sports load and some kidney disease can be the cause of its presence in the results of urine tests.
Glucose
Norma:
|
negative |
in a regular sample |
|
0.06-0.83 mmol/L |
24h sample |
Deviation:
|
high |
causes may include: uncontrolled diabetes, adrenal problems, liver damage, brain injury, substance poisoning or kidney disease; |
|
found |
the use of intravenous fluids can cause glucose in the urine; |
|
Found pregnant |
norm if the pregnant woman is generally healthy. |
Glucose is a type of sugar in the urine. The norm is no or a small amount of glucose in the urine, If the blood sugar level is very high, as in uncontrolled diabetes, the sugar gets into the urine.Glucose can also be detected in cases of kidney disease or disease.
Ketones
Normal: not found or <0.5 mmol / L
Deviation:
|
found |
reasons: a) diabetic ketoacidosis; b) uncontrolled diabetes, alcoholism, isopropanol poisoning; c) a very low carbohydrate diet; d) fasting or eating disorders (anorexia, bulimia); |
|
found in a pregnant woman |
norm if the pregnant woman is generally healthy. |
Ketones are found in urine, if food is not ingested for 18 hours or more, the causes may be illness, vomiting.
Diets low in sugar and carbohydrates, as well as fasting produce ketones in the urine. When detecting the presence of a ketone in the urine, it is very important to determine the blood sugar level to rule out diabetes.
Urobilinogen
Rule: Unfound or < 17 μmol/L
Deviation:
|
elevated |
liver diseases: cirrhosis, hepatitis, hematomas |
|
lowered |
renal failure or blocked bile flow |
Is formed as a result of the collapse of bilirubin.












